Introduction
There is a consensus that the pass rate for first-timers taking the Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA Exam is about 50 percent (i.e., the failure rate can be as high as 50 percent). To increase the chances of passing, you will need to understand the exam topics. This blog post will attempt to do just that – review the CCNA Exam topics, and give some guide on how to study and pass the exam in just one trial.
I will share the highlights of key concepts I made sure I understood before taking the exam to pass it (on my first trial) and include them in the review of each of the sections – including labs. The concepts you need to pay attention to, and things you need not worry about or waste so much time on.
As an overview, the CCNA is Cisco’s most popular certification, a high-in-demand associate-level certification exam that covers foundational concepts in Networking. It helps candidates develop skills for a career in networking and other fields like cybersecurity, clouds, etc., where such knowledge is instrumental.
The CCNA Exam Modules (Sections)

According to the latest version of the CCNA exam topics, there are 6 modules or sections of the exam. Each of these modules is weighted differently in the exam and covers a range of topics and lab demonstrations. The modules and the estimated number of questions are
- Networking Fundamentals – weighted 20% (or 18-21 questions in the exam)
- Network Access – weighted 20% (or 18 -21 questions)
- IP Connectivity – weighted 25% (or 22-27 questions)
- IP Services – weighted 10% (or 9-11 questions)
- Security Fundamentals – weighted 15% (or 13 -16 questions)
- Automation and Programmability – weighted 10% (or 9 -11 questions)
The CCNA exam will typically have between 90-106 questions for a 120mins duration. These may include lab questions, “drag and drop”, simulations, or just plain multiple choice.
1. Network Fundamentals
Networking fundamentals are the most basic introduction to the networking environment. The screenshot of the topics under network fundamentals is shown below.
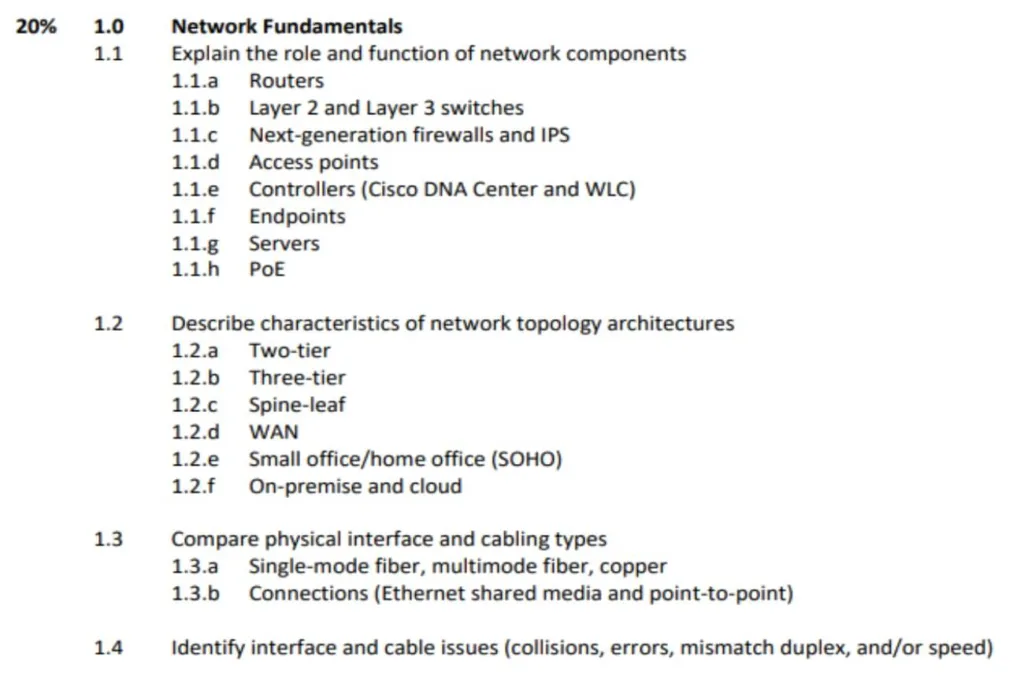
1.1 The Role and Function of Networking Components
Cisco expects you to Explain the role and function of the different networking equipment listed in the section. You should know that routers are layer 3 devices while switches are layer 2 devices. You should know their functions such as routers using IP addresses, having fewer ports, and switches using Mac Addresses with more ports.
Also, the functions of Next-Generation Firewalls in Security, IPS as a warning and prevention system, Access Points in wireless networks, the Function of controllers in an enterprise environment, and the role and function of Power-over-Ethernet in delivering power to devices that are difficult to reach. Less emphasis should be on the fine details of the different standards.
Keywords – Explain, Role, Function
1.2 Characteristics of network topology architectures
Cisco expects you to be able to describe the characteristics of the different network topologies architectures. You should be able to identify the different topology diagrams (i.e. the way devices are arranged in each of the architectures).
You should know the characteristics and number of layers in each of the different architectures, the kind of devices at those layers, and how these work. Spine-leaf architecture is a common feature in practice questions, you should understand how the connections work in them.
Know what WANs are and be able to describe the network architecture in SOHO and WAN. Understand the important WAN technologies such as Leased Lines (using Hub and SpokE topology) and MPLS.
On-prem and Cloud deployment are common features in practice exams. Know their characteristics and should be able to do easy “drag and drop” matchups in comparisons.
Keywords: Describe, characteristics
1.3 Physical Interface and Cabling Types
Cisco expects you to Compare the different interfaces and cabling types. No need to pay too much attention to the fine details of cabling standards.
You should understand fiber optics(single mode and multi-mode) connections and their advantages over copper cabling – the limitations of Copper UTP, electromagnet interference, etc. about connections – cross-over and straight-through.
Connections, Point-to-point, and internet-shared media comparisons.
Keywords: compare
1.4 Interface and cable issues (collisions, errors, mismatch duplex, and/or speed)
Cisco expects you to be able to identify the different interface and cable issues (collisions, errors, mismatch duplex, speed). What can cause these errors e.g. faulty cable, length, wrong duplex/speed settings? Speed mismatch will for example cause a complete shutdown while duplex mismatch will not.
You should know about runts and input errors, giants, Cyclic Redundancy checks CRC, etc. Know what causes them and their impact on the network.
You can be given a screenshot of a configuration output and be asked to identify what the problem may be with the network. The knowledge gained here can also be used to troubleshoot networks based on the type of error in the output.
Keywords: Identify

1.5 Compare TCP to UDP
Know the difference between TCP and UDP when you will typically use one instead of the other. TCP for reliability, UPD for speed, and Know the port numbers for each.
You need to know which protocol uses TCP only, which uses UDP only, and which protocol can use both. Know about the 3-way handshake in TCP connection. It is helpful to be able to do a “drag and drop” type of questions based on UDP/TCP protocol.
Keywords: compare
1.6 Configure and Verify IPv4 addressing and subnetting
Cisco expects you to be able to configure and verify IP addresses. You must understand subnetting as a whole. How to convert binary to dotted IP address scheme and vice-versa. You should know how to verify IP addresses using the CLI of a networking device. This also doubles as a practical lab in many cases.
Keywords: Configure, verify
1.7 Describe the need for private IPv4 addressing
You are to describe the need for private IPv4 addressing due to the limited number of IP addresses. Know the different IP address Classes (from subnetting) and Private IP addresses. Private IP addresses are not routable.
Keywords: describe
1.8 Configure and Verify IPv6 Addressing and Prefix
Configure and Verify IPv6 Addressing and Prefix, learn the IPv6 addressing format, how to shorten or abbreviate long IPv6 addresses (and vice versa), how to find the IPv6 prefix (global unicast address) take note of the bits, how to configure IPv6 address both using the long and the short form of the address, also, configuring IPv6 using the EUI-64.
You should also be able to identify both valid and invalid IPv6 addresses based on the convention for abbreviating them. It is common in practice exam scenarios.
Keyword: configure and verify
1.9 Describe IPv6 Address Types
Describe the various types of IPv6 Unicast addresses (Global, Unique local, and Link Local addresses), Anycast, and multicast addresses. Earlier CCNA exam topics specifically mentioned that you compare the various types of IPv6 addresses.
You should also be able to describe the EUI-64 IPv6 address and how to convert a 48-bit MAC address to this 64-bit interface identifier. As a side information, know that MAC addresses are composed of two parts and what these parts are. Know which types of IPv6 addresses are routable and which are not. Learn the multicast address scopes.
Keyword: describe
1.10 Verify IP Parameters For Client OS (Windows, Mac OS, Linux)
Know the commands for verifying IP commands for Windows, Mac OS, and Linux. For example, Windows uses ipconfig/ all to show all the IP parameters from the Windows command prompt, while Linux uses the ifconfig command.
You should also be able to use these commands to identify the broadcast address, device IP, Mac address, Gateway IP, etc, or identify various IP parameters from a screenshot of a command prompt.
keyword: verify
1.11 Describe Wireless Principles
Description of the fundamentals of Wireless Networks especially as they compare to Wired Networks e.g. Using CSMA/CA in preventing collisions in Wireless Networks compared to CSMA/CD in Wired Networks. Learn the basics of Wireless Radio Frequency (RF), the two frequency bands used in Wireless Networks (2.4Ghz and 5Ghz), Channels, and their overlaps.
Know the recommended channels 1, 6, and 11 in the 2.4 GHz to avoid interference. The non-overlapping channels in the 5GHz, learn the 802.11 standards, their frequencies, theoretical data rates, and common names. Learn the different Service Set types and SSIDs,
Wireless Network Encryption methods such as WEP, TKIP, CCMP, GCMP, and where they are commonly used.
Keyword: describe
1.12 Explain Virtualization Fundamentals (Server Virtualization, Containers, and VRFs)
Explain the basics of virtualization, server virtualization, types, Type 1 Hypervisor(VMM), Type 2 Hypervisor, and why virtualization. Learn about the basics of Containers (Docker) and how they differ from a VM. Learn the basics of Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) and its capabilities.
Keyword: describe
1.13 Describe Switching Concepts
Ethernet LAN switching; Mac Address learning and Aging, MAC Address switching, Mac Address Flooding, MAC address table. Know how the Mac Address table is populated, how a switch learns the Mac address, and the ARP process.
Also, you should know how the Source and Destination Mac address change as messages traverse the network ( unlike Source IP and Destination IP which remain the same, the Source and Destination Mac Address changes as the frame is moved from one device to another).
2. Network Access

2.1 Configure and verify VLANs (normal range) spanning multiple switches
It is expected that you can configure and verify labs for VLANs. Naming the VLANs, assigning different interfaces across multiple switches to different VLANS, and testing connectivity between multiple VLANs.
Also, how to use the show VLAN command to check how the VLANs are assigned. Know what an access port is (and how it differs from a trunk port,), IP Phones, and Voice VLANS; how you configure both voice and data on an Access port.
Prepare adequately for the practical exam
Keywords: configure, verify
2.2 Configure and verify inter-switch connectivity
Cisco expects you to know what trunk ports are(a port that is assigned to multiple VLANs), and how they differ from Access ports(assigned to a single VLAN), configure and verify trunk ports, and the default setting for old and new switches.
Know VLAN Tagging and the 802.1Q. As part of the configuring of trunks, you should know how to enable Trunking on a Cisco switch that does not support trunking using the switchport mode trunk and switchport nonegotiate interface configuration mode commands,
It is important to know how the interface modes are negotiated (dynamic auto, dynamic desirable, access, trunk). It will help you answer drag-and-drop questions on DTP (although not explicitly stated in the blueprint but is a common feature in practice exams.
Keyword: configure, verify
2.3 Layer 2 discovery protocols
It is expected to know how to configure and verify both CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) and LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol). The differences between the two protocols (for example. CDP is Cisco proprietary and is only supported on Cisco Devices while LLDP is open standard), know the similarities in terms of configuration as well as the differences.
You should be able to identify the output from the two commands by looking at the subtle differences between the two. Know the hold time for each, global configuration command, interface-level command, etc.
Keywords: Configure, verify
2.4 EtherChannel (LACP)
Configure and Verify Layer 2 and Layer 3 EtherChannel – LACP. Know what EtherChannels are, how they work, why we have them, and the conditions that must be met before you can successfully configure EtherChannel. Etherchannel Load-balancing, The focus is on LACP. Pay less attention to PAGP.
Keywords: configure, verify
2.5 Describe the need for and basic operations of Rapid PVST+ Spanning Tree Protocol and identify basic operations
Understand why we need the Spanning Tree Protocols, be familiar with the different standards and their common designations, and Know the different port names and what they do – root port, root bridge, root guard, etc. Port states – (Blocking and forwarding) and Portfast.

2.6 Describe Cisco Wireless Architectures and AP Modes
It is expected that you can describe the common Cisco Wireless Architecture – Autonomous AP, Cloud-based, and Split-MAC wireless, the different AP modes Local (the default), Flexiconnect, Bridge modes, the different management modes – sniffer mode, monitor mode, SE-connect mode, rogue detector mode, etc.
Cisco practice questions will for example describe a mode or function and then ask you to identify the mode being operated. Flexiconnects and bridge modes are a regular feature in practice exams or simulations
Keyword: describe
2.7 Describe physical infrastructure connections of WLAN components (AP, WLC, access/trunk ports, and LAG)
Describe how the different devices listed above are connected in the physical infrastructure of a Wireless LAN network (WLAN), and know which segment of the infrastructure uses an Access or a Trunk port.
Know what type of connection AP use for example Access or Trunk? How about WLC? Access or Trunk, Describe how LAG aggregates multiple single connections into a single bundle or aggregate to provide redundancy and increased bandwidth.
Keyword: describe
2.8 Describe AP and WLC management access connections (Telnet, SSH, HTTP, HTTPS, console, and TACACS+/RADIUS)
Cisco expects you to be able to describe how a network administrator can access and manage the Access Points (AP) and the Wireless LAN controller (WLCs) in the network using protocols such as Telnet, SSH, HTTP/HTTPS, console, TACACAS+/RADIUS.
It is important to know the differences between TACACS+ and RADIUS including the Port numbers they each use. Also, be aware of which of the protocols listed are secure and which of them are not.
2.9 Configure the components of a wireless LAN access for client connectivity using GUI only such as WLAN creation, security settings, QoS profiles, and advanced WLAN settings
The configuration here is using the Graphical User interface. Know the basic WiFi network topology and how the different devices can be connected. For example, WLC connects to a switch via LAG (Link Aggregation Group) and it only supports Static LAG,(no PAgP or LACP). know about the CAPWAP tunnel, the different WLC ports, and interfaces.
Know what the function of the different interfaces and ports is. It is not likely for you to do a Wireless LAN configuration of this in the exam but you should be able to identify the different settings in GUI. Pay attention to the security settings – QoS profile and advanced settings.
Keywords: configure, GUI
3. IP Services

3.1 Interprete the Components of a Routing Table
Cisco expects you to know the basics of routing fundamentals and then interpret the components of the routing table, routing protocol code, Metric, and Administrative distance, how they differ, and which of them take precedence in the routing process, Gateway of last resort, etc.
3.2 Determine How a Router Makes a Forwarding Decision by Default
Understand how factors such as Longest Prefix match, Administrative Distance (AD), and Routing protocol metric affect the packet forwarding decisions. Which of them takes precedence?
You should know the different routing protocol metrics for all the common routing protocols – OSPF, RIP, EIGRP (internal and external), Static route, etc
3.3 Configure and Verify IPV4 and IPV6 Static Routing
Know how to configure and verify Static routes, either by using the next hop IP address or by using the exit interface. Understand what the default route is for both IPV4 and IPV6 addresses, network route, and host route. It is not unusual to have practical lab simulations in the practice exam. Try as much as possible to do the practice labs using packet tracer labs.
Keywords: Configure, verify
3.4 Configure And Verify Single Area OSPFV2
Know all the conditions that must be fulfilled to form OSPF neighbor relationships e.g. Area ID, Hello and Dead Timers, Subnet, etc.
Know how neighbor adjacencies are formed, configuring, OSPF costs, how to activate OSPF on an interface, configure point-to-point, Broadcast, selection of BDR/DR Selection, Router ID – how you get the router ID. Know how to identify these from a configuration output. Also, understand that the Router ID is different from the Process ID.
Keywords: configure, verify
3.5 Describe the Purpose, the Function, and the Concepts of First Hop Redundancy Protocols
You also know some basic information about the other common types of FHRP such as Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP), Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) which is a Cisco Proprietary product, and the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP).
Know the common terms used in describing each of these e.g. active and standby routers in HSRP, Master and Backup in VRRP, AVG/AVF in GLBP, etc. Know the Mac Addresses they use.
You do not have to learn how to configure them.
4. IP Services
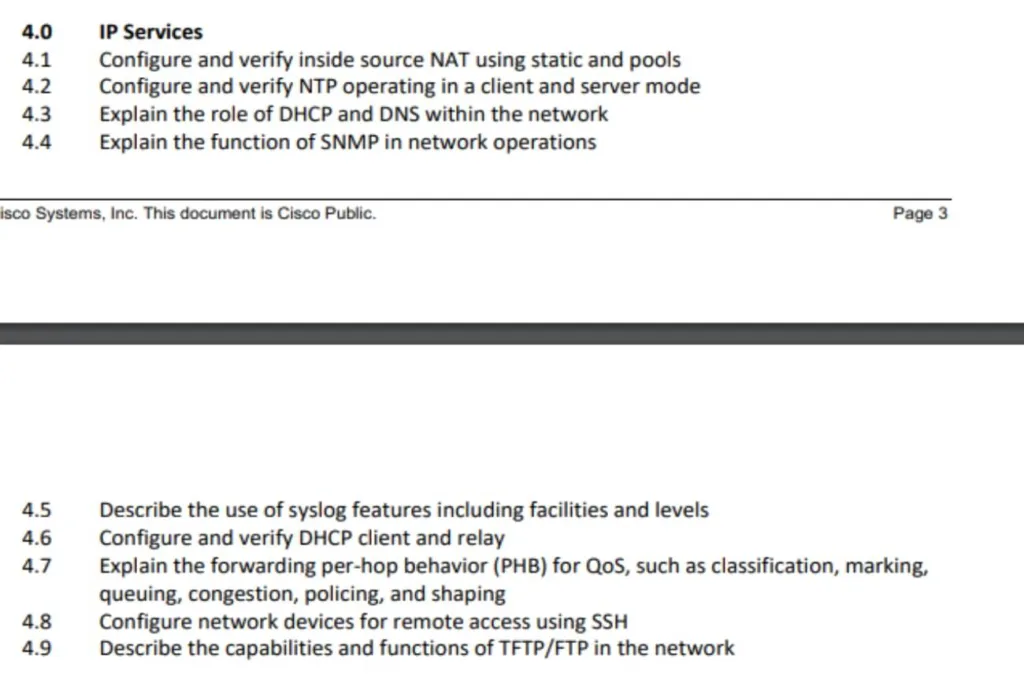
4.1 Configure And Verify Inside Source NAT using Static and Pools
First, you must understand why you need Network Address Translations (NAT) – IPV4 Address exhaustion and how the NAT process takes. place. Know the private IP address ranges, and how to identify the different types of addresses in NAT – inside local, inside global, outside local, and outside global. Know the static and dynamic NAT.
Configure and verify NAT using static and Pools. Know how to create the address pools and how to exclude addresses from the pool.
Keywords: configure, verify
4.2 Configure and Verify NTP Operating in Client and Server Mode
Know the difference between the Client and Server mode in Network Time Protocol, Know the default mode, and the difference between the two modes. Learn how to configure both and verify NTP operating in Client and Server Mode. Other basic NTP configurations are included.
Keywords: configure, verify
4.3 Explain the Role of DHCP and DNS within the Network
Know how DHCP allocates addresses dynamically within a network and the function of DNS in mapping IP addresses to domain names(address resolution). Know the different types of DNS records such as A, AAAA, CName, NS, and Txt records.
4.4 Explain the Function of SNMP in Network Operations
The details such as how to set it up are not required, just know its role and purpose in Network operations. Also, know about the two types. of devices in SNMP, the managed devices, and the Network Management system NMS (SNMP Server).
Learn about the components of SNMP – SNMP Agent, MIB, etc. SNMP messages – SNMP trap and Inform, Set, Get, GetNet, Getbulk, and message class these messages belong to. Which of them are sent by managed devices and which are sent by the NMS?
Keywords: explain
4.5 Describe the Use of Syslogs Including Facilities and Levels
Know what Syslogs are and how they work, know the Syslog formats (Seq, Timestamp, facility, severity, Mnemonic, etc), and know the various Syslog facilities and severity levels.
Know the 8 severity levels (0 -7 ), including their names e.g., for example, level 0 is emergency, 1 is alert, 2 is critical, 7 debugging, etc. It is helpful to use memory to help you remember these levels as they may be important for the exam. It is helpful to use mnemonics to memorize these levels
4.6 Configure And Verify DHCP Client And Relay
Know the difference between the two and how to configure and verify them. Why is a router acting as a relay agent and when is it acting as a DHCP client? Take note of the placement of the routers in the router for it to act as a relay agent or as a DHCP Client.
Keywords: Configure, verify
4.7 Explain the forwarding per-hop behavior (PHB) for QoS such as classification, marking, queuing, congestion, policing, shaping
Explain the basics of QoS and how it works, using QoS in managing network characteristics like Bandwidth, Delay(one-way and 2-way delays), Jitter, and Loss. QoS Queuing (FIFO), Tail drop, TCP global synchronization.
Know how to prevent Tail drop and TCP global synchronization using Random Early detection RED, Weighted Random Early Detection WRED. Explain Classification and Marking, Classification methods such as using ACLs, NBAR, Priority Code Point PCP, Differentiated Service Code Point (DSCP), and Congestion management. Shaping, and Policing.
Keyword: explain
4.8 Configure network devices for remote access using SSH
Know what SSH is, and how to connect to a device remotely and securely using SSH. It is important to know how to configure SSH – including how you generate RSA keys, Vtty lines, passwords, usernames, SSHv2, etc.
Also be aware of the fact that before you can generate the RSA keys, you must have configured the hostname and DNS domain name. It is also helpful to be aware of Telnet as a less secure way to remotely connect to a device.
Keyword: configure
4.9 Describe the capabilities and function of TFTP/FTP in the network
Understand the purpose of these two protocols and the differences between them. Take note of their protocol numbers, which of them is more secure as well as other basic differences between them. You do not need to learn the configuration at the CCNA level.
Keyword: describe.
5. SECURITY FUNDAMENTALS
The CCNA is not a security certification, much of what is required to pass the security fundamentals are basic security concepts. Only a few configurations are in the exam blueprint.

5.1 Define key security concepts (threats, vulnerabilities, exploits, and mitigation techniques)
The CCNA exam demands that you know the definition of Key security concepts of threats, vulnerability, exploits, and mitigation techniques. This should also include the CIA Triad – the Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability of Network resources as the foundation of security.
Mitigation techniques deal with how you protect against threats to the network – restricting physical access, locks, implementing firewalls, antimalware, etc.
Keywords: define
5.2 Describe Security Program Elements
Describe user awareness programs, training programs, and physical access control. Know the difference between awareness and training, and the form they take (training is more formal unlike Awareness programs).
Keyword: describe
5.3 Configure and verify device access control using local passwords
Configure local passwords on devices, password encryption, enable secret and enable password commands, which take precedence?, password encryption command, (MD5 and MD7), etc. Console password, Line Vtty password, etc.
Keyword: configure
5.4 Describe Security Password Policy Elements
The CCNA exam expects you to be able to describe Security password policy elements in terms of management and complexity. Password alternatives such as the use of Digital certificates, Biometrics, and multifactor authentication (MFA).
Pay attention to MFAs. For example what factors (“Something you know”, “Something you have”, “Something you are”) combinations constitute an MFA and what does not?
Keyword: describe
5.5. Describe IPsec remote access and site-to-site VPNs
Describe how you secure connections over the internet using VPNs; Site-to-site VPNs using IPSEC and Remote Access VPNs using TLS. Learn about the GRE over IPSEC, TLS VPN tunnels, etc. Know the difference between the Remote access VPN and Site-to-site VPN.
5.6 Configure and verify access control lists
Know what ACLs are, their basic purpose, the ACL logic, and the types of ACLs. Take note of the numbering ranges for the types including the ranges for extended ACLs. Configure and verify standard-numbered ACLs and standard-named ACLs – including how to edit ACLs.
Keyword: configure
5.7 Configure Layer 2 security features (DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP inspection, and port security)
Configure DHCP snooping, Dynamic ARP Inspection, and Port Security. Know what trusted and untrusted ports are in the network.
Learn the basics about the common security attacks on a network and how you can prevent them, Examples include DoS attacks, Spoofing attacks, Man-in-the-middle attacks, Reflection/Amplification attacks, Social engineering attacks, Malware, reconnaissance attacks, and password-related attacks.
Keyword: configure
5.8 Differentiate authentication, authorization, and accounting concepts
Know the definition, differences, and specific examples of Authentication (verifying a user’s identity), Authorization (granting a user the appropriate access and permission), and Accounting (taking a user’s activities). Know about ISE (Identity Service Engine) – Cisco’s AAA server for controlling and monitoring users.
Learn about the two protocols supported by ISE – RADIUS and TACACS+
5.9 Describe wireless security protocols (WPA, WPA2, and WPA3)
Describe the Wifi Protected Access as developed by the Wifi Alliance (WPA, WPA2, and WP3), the two authentication modes supported by these – Personal mode using PSK and Enterprise Mode using 802.1X with an authentication server.
Know the type of authentication and encryption used for each of WPA, WPA 2, and WPA3. You should be aware of PMF, SAE, and Protected secrecy in WPA3.
5.10 Configure WLAN using WPA2 PSK using the GUI
Basic configuration using the Graphical user interface (GUI)
Keyword: configure
6. AUTOMATION AND PROGRAMMABILITY
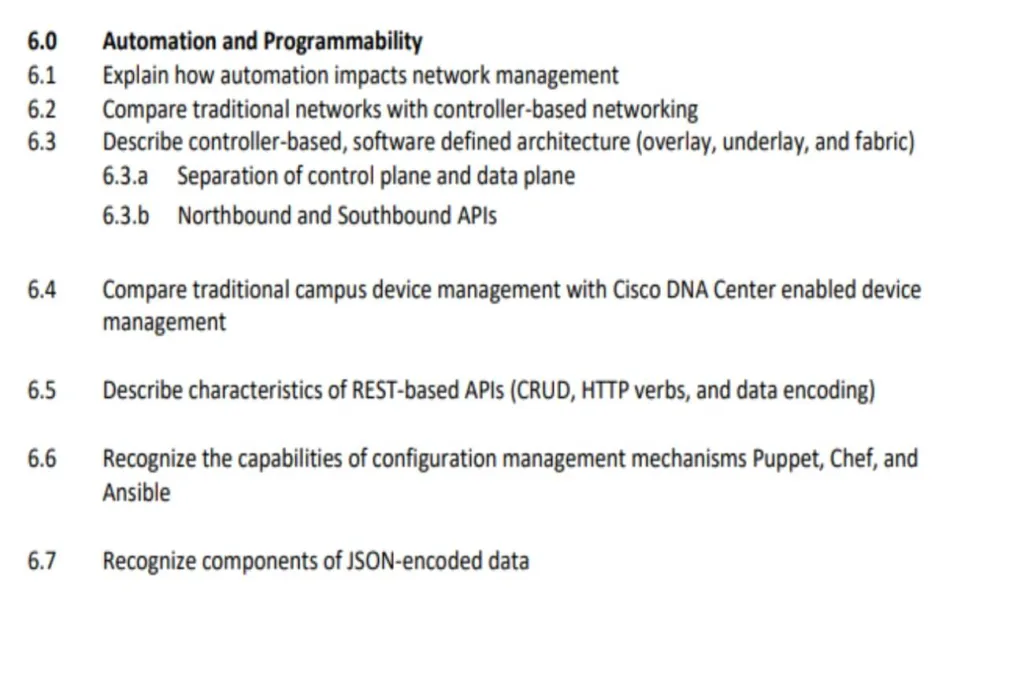
6.1 Explain how automation impacts network management
You should be able to explain what Network Automation is and its benefits and know the downside of managing networks manually(traditional model), e.g. reducing human errors/typos, increasing scalability, standardizations, etc Know the impact of Automation regarding Opex (Operational expense).
Keyword: expense
6.2 Compare Traditional Networks with Controller-based Networking
Understand the Logical Planes of network functions to be able to compare Traditional Networks with Controlled-based networking. Know the appropriate examples of functions at the Data (Forwarding), Control, and management planes.
It is also noteworthy that the CPU processes the operation of the Control and Management planes while the Data plane is processed by specialized hardware called ASICS (for speeds) and that the MAC address is stored in TCAM (Ternary content-addressable Memory).
Of much importance is to note that Traditional Networks generally use a distributed control plane and that Controller-based Networking uses a centralized control plane.
Keyword: compare
6.3 Describe controller-based and software-defined architectures (overlay, underlay, and fabric)
The CCNA expects you to be able to describe what is Software Defined Networking SDN, the different layers (the Application layer, Control layer, and Infrastructure layer), and the components of each of these layers.
You should also be able to describe what a Controller is, the Southbound Interface SBI including Cisco’s OpenFlow, OpFlex, Onepk, and NETCONF, the Northbound Interface, and REST APIs.
Study a Specific example of SDN i.e. Cisco SD-Access Describe Underlay, Overlay (specific mention of SD-Access using VXLANS), and Fabrics (which is a combination of both Underlays and Overlays). Describe the details of the Cisco DNA Center which is the Controller in SD-Access.
Keyword: describe
6.4 Compare Traditional Campus Device Management With Cisco DNA Center Enabled Device Management
Compare the Cisco DNA Center and the Traditional Network Management.
6.5 Describe characteristics of REST-based APIs (CRUD, HTTP verbs, and data encoding)
Describe the Characteristics of REST APIs, CRUD operations, HTTP verbs, HTTP Requests, and HTTP responses, Know what the common HTTP response code means e.g. 1xx – Informational,4xx is a Client error, 5xx is a Server error, etc.
6.6 Recognize the capabilities of configuration management mechanisms Puppet, Chef, and Ansible
A basic introduction to configuration management tools. Know some specific details Ansible, Puppet, and Chef. Ansible (agentless, written in Python, uses a push model, Playbook, YAML, etc), Puppet (written in Ruby, uses a Pull model, Agentless, Manifest and Templates as text files, etc), Chef (Agent-based, Pull model, textfiles as resources, cookbooks, and recipes, etc).
6.7 Interpret JSON encoded data
You should be able to interpret JSON-encoded data and spot common errors in them. Know the format.
Conclusion
Understanding what Cisco requires of you is one of the most helpful keys to passing the CCNA exam on your first trial. Understand what type of information will be helpful in the exam – Some of the sub-topics are explicitly stated while others are implied.
Also, understand which keywords like configure, describe, explain, verify, etc to give you an idea of what you need to know. The different sections above, while not exhaustive, gave some insights into what you need to know to pass the CCNA exams.
Considering Cisco certifications, you may want to read: CISCO’S ASSOCIATE LEVEL CERTIFICATIONS: WHICH IS THE BEST FOR?
Credit: Cisco.com for the material and references.




